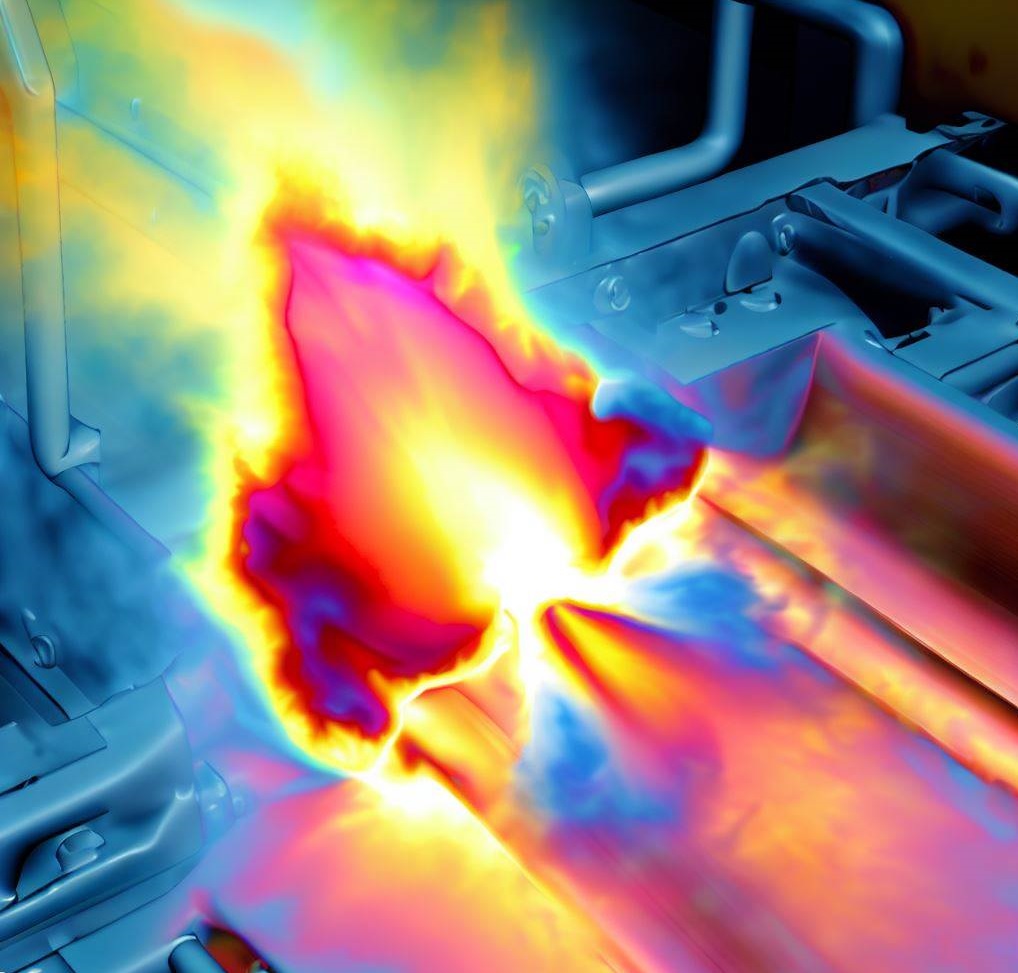
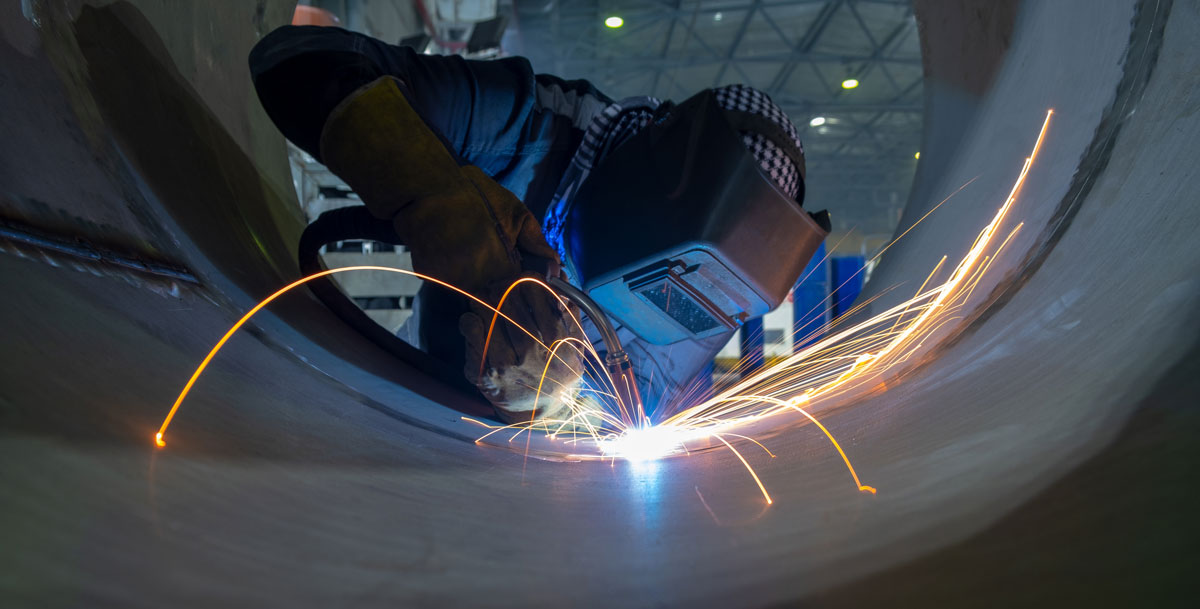
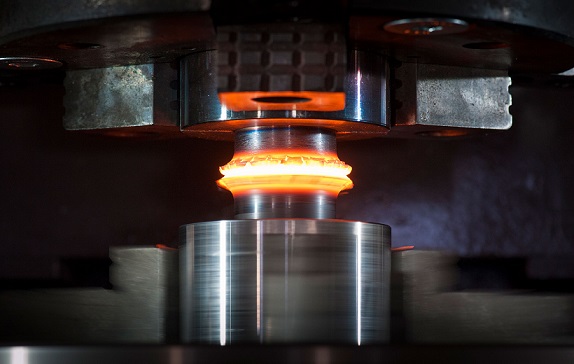
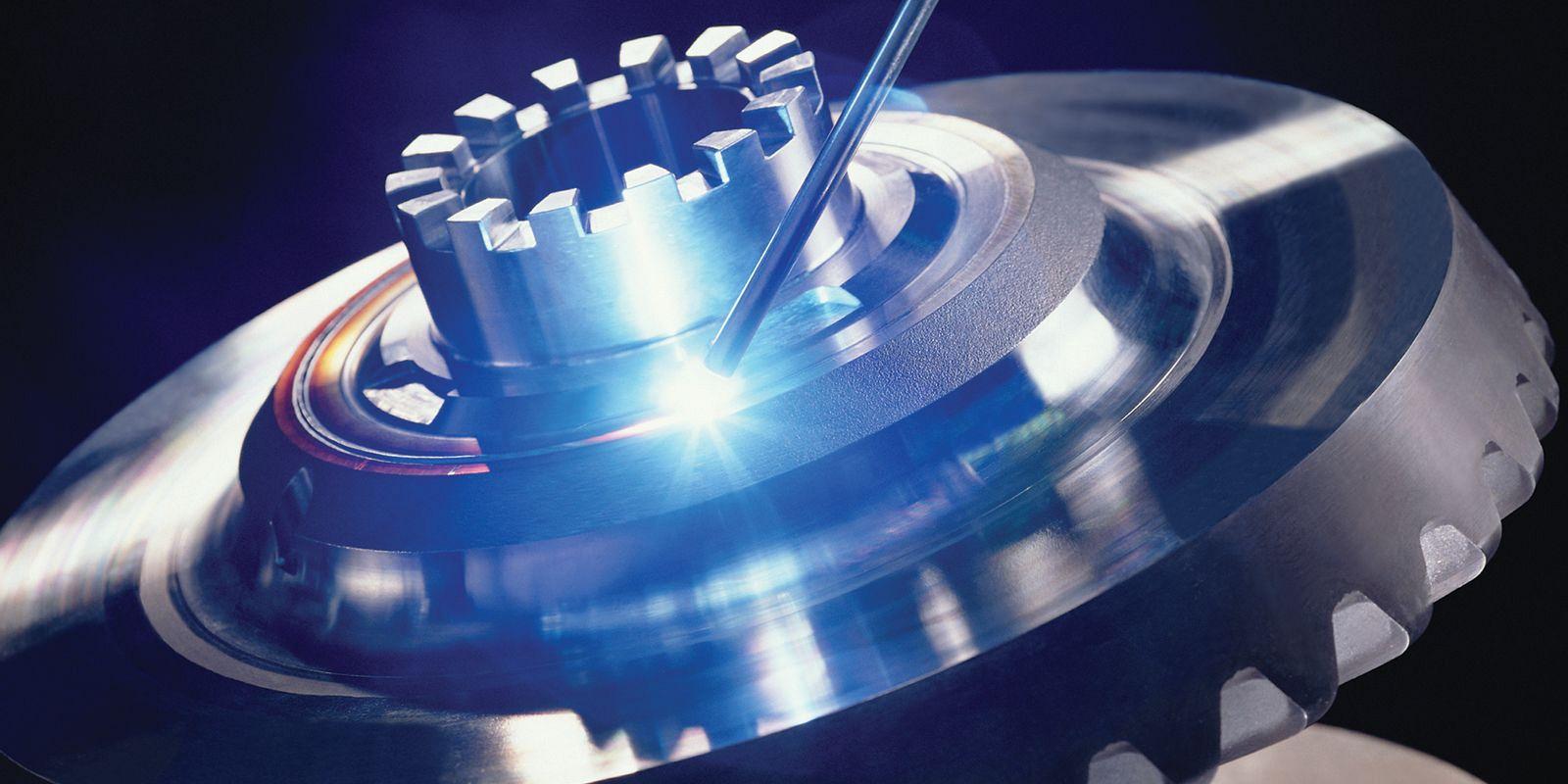
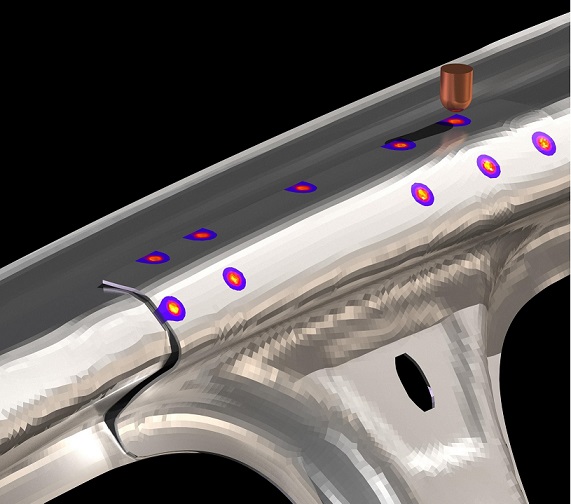
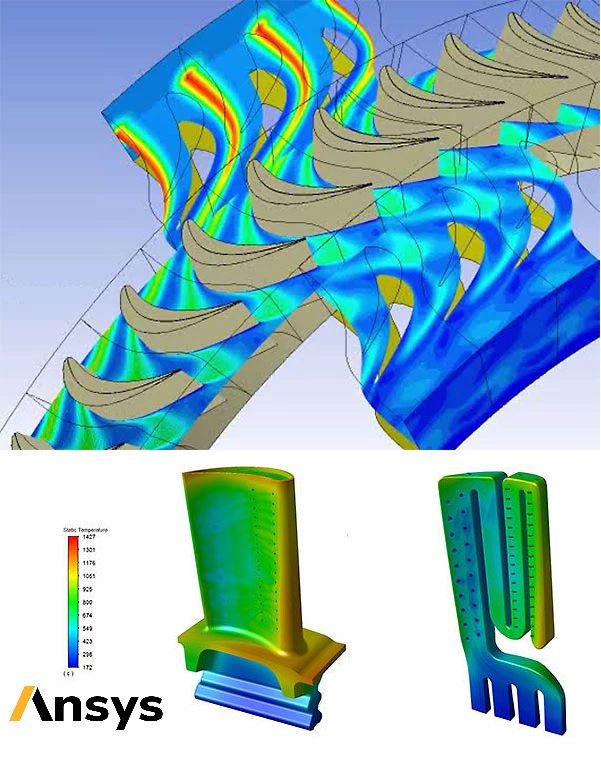
Laser beam welding is a process that uses a high-energy laser beam to heat and weld metal components together. The laser beam is directed at the joint between the components, melting the metal and creating a strong, precise bond. One of the advantages of laser beam welding is its relatively narrow heat-affected zone, which helps minimize distortion and damage to the surrounding material. This makes it a popular choice for welding thin materials, such as those used in the aerospace and medical industries.
Electron beam welding is a similar process that uses a high-energy beam of electrons to melt and weld metal components together. The electron beam is focused onto the joint between the components, creating a high-intensity heat source that melts the metal and creates a strong, precise bond. Like laser beam welding, electron beam welding can produce precise welds with a narrow heat-affected zone. It is often used in high-tech applications such as the aerospace and semiconductor industries.
Both laser beam welding and electron beam welding offer several advantages over other welding processes. They are both highly precise, and their narrow heat-affected zones help prevent distortion and damage to surrounding materials. However, both processes require specialized equipment and expertise, which can make them more expensive and difficult to use than other welding methods.